Tackling Complex Data
Robust Algorithms across Sources, Inputs, and Noise

In Challenge Event 2, the data size significantly increased in size.
Additional data types were added to the training data’s complexity.
To win a prize, teams’ performance exceeded the specified baseline algorithm as well as specificity, sensitivity, and lead time thresholds.
Technical Challenge Elements
| Multiple Data Sources With varied source populations, patient demographics, types of injury, and standard clinical operating procedures. Each data set had a different standard set of sensor readings, with different added sensors in each phase of the DARPA Triage Challenge. Approaches demonstrated robustness across a range of datasets and sensor types. |

| Multiple Data Inputs Included static data (e.g., mechanism of injury or anatomical injury pattern); multiple simultaneous, continuous streams of high-frequency waveforms; and potentially point-of-care imaging data. |
| Raw Data Data from the sensors (i.e., without any post-sensor cleaning), with the noise, aberrant values, and dropouts that occurred in clinical environments. |

| Degraded Data DARPA injected additional challenges that can be expected in battlefield and civilian pre-hospital settings, such as noisy, aberrant values, severe degradation or total loss of a particular sensor, to test the robustness of competitor strategies to such plausible scenarios. |
Life Saving Interventions (LSIs) are a medical care resource, activity, or procedure used to sustain life. LSIs have been grouped by type of injury and/or mechanism of treatment:
- Airway & respiration: Intubation, Cricothyroidotomy, Laryngoscopy, Mechanic Ventilation
- Bleeding control: Tourniquet, Pelvic Binder
- Blood products: Packed Red Blood Cells, Plasma, Whole Blood Transfusion
- Chest decompression: Needle Decompression, Chest Tube Management
- Neurologic products & procedures: Craniotomy/Craniectomy, Hypertonic Saline, Antiepileptic Medications
- Damage control procedures: Thoracotomy, Exploratory Laparotomy, IR Embolization
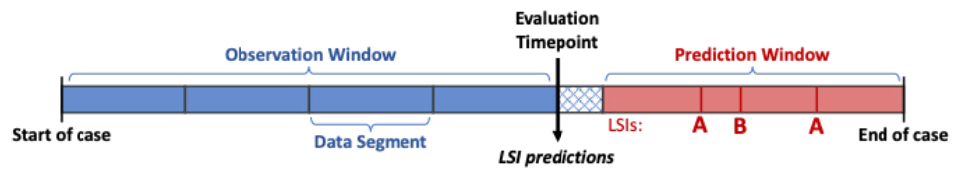
Illustration of evaluation within a single case.
Solutions are provided with data in sequential data segments containing timestamped health record and physiological signals data. The end of each data segment serves as an evaluation timepoint, where solutions generate predictions using data within the preceding observation window comprised of one or more data segments. LSI predictions are compared against the set of timestamped LSIs that occur in the future within the prediction window, excluding a predetermined minimum lead-time after the evaluation timepoint.
In this example, the set of ground truth LSIs is [A, B], excluding any other LSIs that occur within the observation window or intervening gap (not pictured).
Qualified funded and unfunded teams participated in the competitions, striving to advance the use of autonomous systems for rapid, stand-off casualty assessment to facilitate timely and accurate medical triage.
- AI TEMPO
- AID3D
- AUSTERE
- CAMA
- Coordinated Robotics
- CRITIC
- Deep Breathe
- LENS
- MSAI
Overview