Unlocking Trauma Data’s Potential
Algorithms for Early Prediction

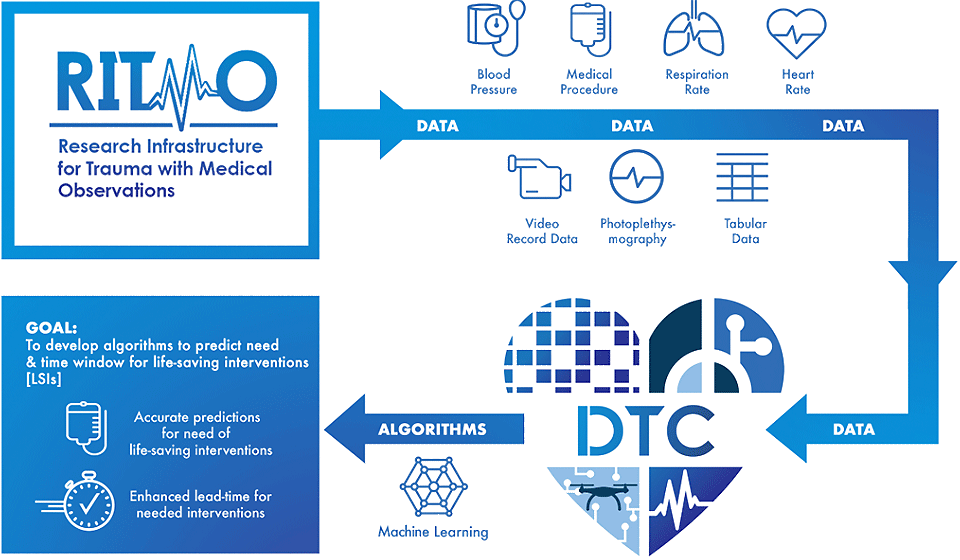
In Challenge Event 1, teams were provided real-world trauma center datasets containing thousands of cases with >500 variables. This data was collected from pre-hospital (medevac, ambulance) until 4 hours after hospital admission. Teams developed algorithms to predict the need for life-saving interventions during this time.
In Challenge Event 2, the data size significantly increased. Additional data types were added to the training data’s complexity. To win a prize, teams’ performance exceeded the specified baseline algorithm as well as specificity, sensitivity and lead time thresholds.
Life Saving Interventions (LSIs) are a medical care resource, activity, or procedure used to sustain life. LSIs have been grouped by type of injury and/or mechanism of treatment:
- Airway & respiration: Intubation, Cricothyroidotomy, Laryngoscopy, Mechanic Ventilation
- Vascular access & monitoring: Peripheral IV, Central Line Maintenance, Arterial Line Maintenance
- Bleeding control: Tourniquet, Pelvic Binder
- Vaso/cardioactive medications: Epinephrine, Dopamine, Phenylephrine, Vasopressin, Hydrocortisone
- Crystalloid products: Normal Saline (>500cc), Lactated Ringers (>500cc)
- Blood products: Packed Red Blood Cells, Plasma, Whole Blood Transfusion
- Cardiovascular procedures: CPR, Defibrillation/Cardioversion, Pericardiocentesis
- Chest decompression: Needle Decompression, Chest Tube Management
- Neurologic products & procedures: Craniotomy/Craniectomy, Hypertonic Saline, Antiepileptic Medications
- RSI sedation medications: Ketamine, Versed, Etomidate, Ativan, Propofol
- Limb salvage: Amputation, Fasciotomy
- Damage control procedures: Thoracotomy, Exploratory Laparotomy, IR Embolization
Performance measured for each case using two metrics:
Jaccard Index (JI): How accurate were the predictions?

Prediction Lead Time (PLT): How early were the correct predictions?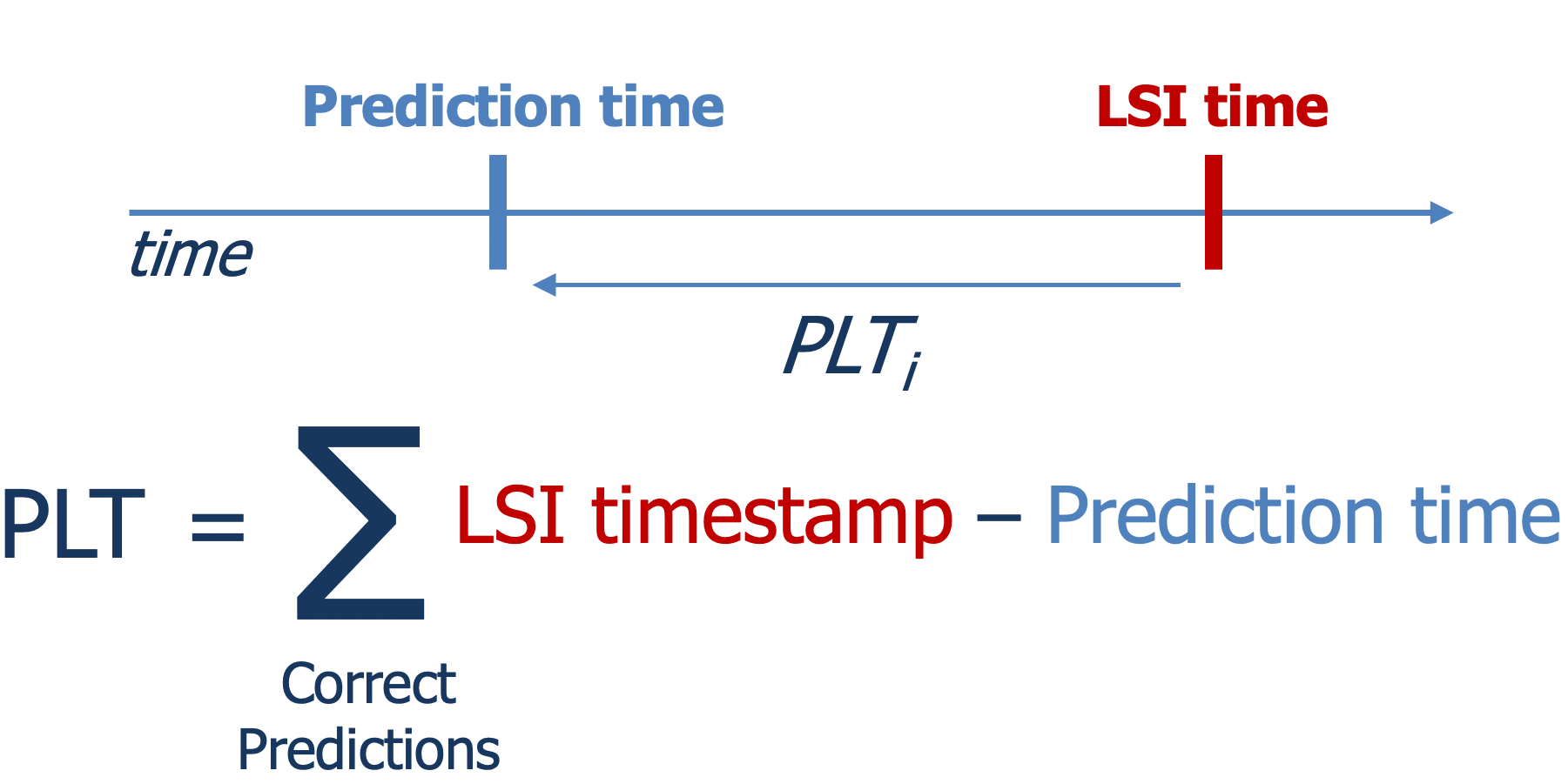
Final ranking was determined based on each team’s event score.
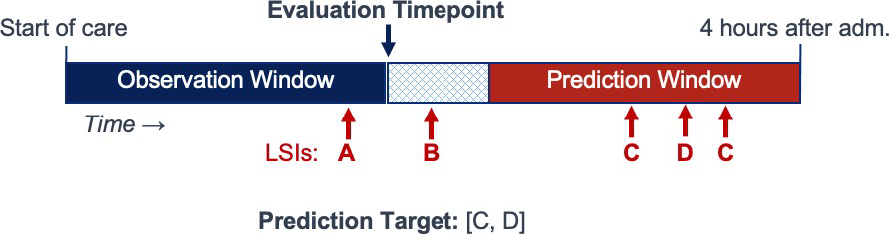
All solutions were evaluated at a predetermined set of evaluation timepoints within each case, where a case encompasses the available pre- and in-hospital data and timestamped LSIs from a single hospital admission. At each evaluation timepoint, timestamped data within the observation window was provided to submitted solutions for the prediction task, where the observation window began with the start of case and ends at the evaluation timepoint.
The prediction target was the unique set of ground-truth LSIs within the prediction window, the time window beginning 15 minutes after the evaluation timepoint and extending to the end of care or four hours after hospital admission, whichever came first.
These innovative data teams developed cutting-edge algorithms to predict life-saving interventions from complex trauma data and ultimately improve medical decision-making.
- AI TEMPO | Alert for Intervention using Timeseries EMergency Physiological Observations | DARPA-funded
- ALICE | AI Life Saving Intervention Compute Engine | DARPA-funded
- AUSTERE | AI User Supporting Triage and Evacuation Recommendation
- CAMA | Center for Advanced Medical Analytics
- CNA | Center for Naval Analyses
- Coordinated Robotics
- CRITIC | Continuous Review and Intervention for Timely Care | DARPA-funded
- LENS | LSI Early Notification System | DARPA-funded
- MGB-Harvard
- MSAI
- Robotika
- TrueFit.AI
Leaderboard
Scoring criteria: Accuracy of LSI prediction (for any LSI and for more specific classifications, such as hemorrhage or airway interventions)
| Teams | Score | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coordinated Robotics* | 625 | 434 | 191 |
| MSAI* | 555 | 364 | 191 |
| CAMA* | 532 | 368 | 164 |
| LENS | 310 | 129 | 181 |
| AI TEMPO | 268 | 91 | 177 |
| CRITIC | 189 | 21 | 168 |
| TrueFit.AI* | 179 | 37 | 142 |
| Robotika* | 143 | 27 | 116 |
| ALICE | 109 | 18 | 91 |
| AUSTERE | 61 | 49 | 12 |
| MGB-Harvard* | 44 | 13 | 31 |
| CNA* | 35 | 8 | 27 |
* Self-funded

Overview