Program Summary
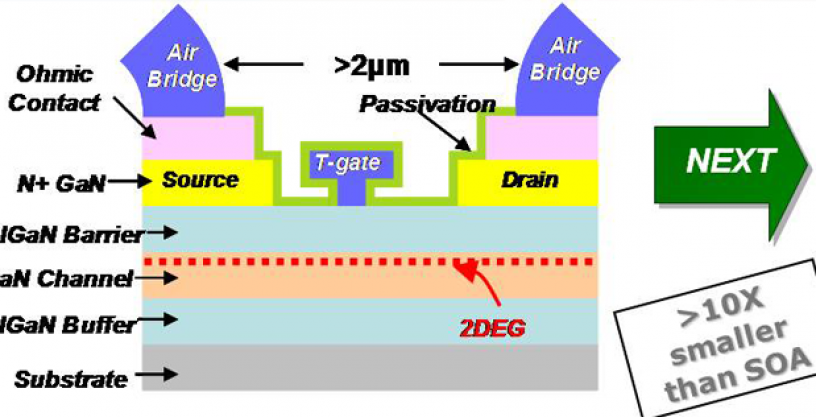
High performance analog, RF and mixed-signal electronics usually require transistors with cutoff frequencies greater than 200 GHz. Current transistor technologies in silicon (i.e., complementary metal oxide semiconductor and silicon-germanium heterojunction bipolar transistor) can achieve such transistor speed, but only with unacceptably small voltage swing and breakdown voltage, severely inhibiting performance. These constraints limit the development of crucial military electronics including high-speed power amplifiers, ultra-linear mixers and high-output power digital-to-analog converters. DARPA's Nitride Electronic NeXt-Generation Technology (NEXT) program aims to develop a revolutionary nitride transistor technology that simultaneously provides extremely high speed and large voltage swing. GaN transistors developed in the NEXT program will result in the development of a manufacturable, high-yield, high-uniformity process that will realize large-scale integration of circuits with 1,000 or more transistors.
NEXT is developing a revolutionary nitride transistor technology that simultaneously provides extremely high-speed and high-voltage swing [Johnson Figure of Merit larger (JFoM) than 5 THz-V] in a process consistent with large-scale integration in enhancement/depletion (E/D) mode logic circuits of 1,000 or more transistors. In addition, the fabrication processes will be manufacturable, high-yield, high-uniformity, and highly reliable. The accomplishment of this goal will be validated through demonstration of specific process control monitor test circuits such as 5, 51, and 501-stage ring oscillators, in each of the three program phases.
Initially, NEXT will develop a manufacturable process to achieve high-speed, high-JFoM devices for both E and D-mode operation. The program will demonstrate the ability to combine these devices into a small logic circuit (on the order of 10 transistors). The program will further increase the speed of the E and D-mode devices and demonstrate the capability to combine these devices into moderate-sized logic circuits (on the order of 100 transistors). Finally, NEXT will realize significant improvements in the yield and uniformity of the nitride transistors and the necessary circuit integration processes to enable large-scale integration (logic circuit on the order of 1,000 transistors).
This program is now complete
This content is available for reference purposes. This page is no longer maintained.